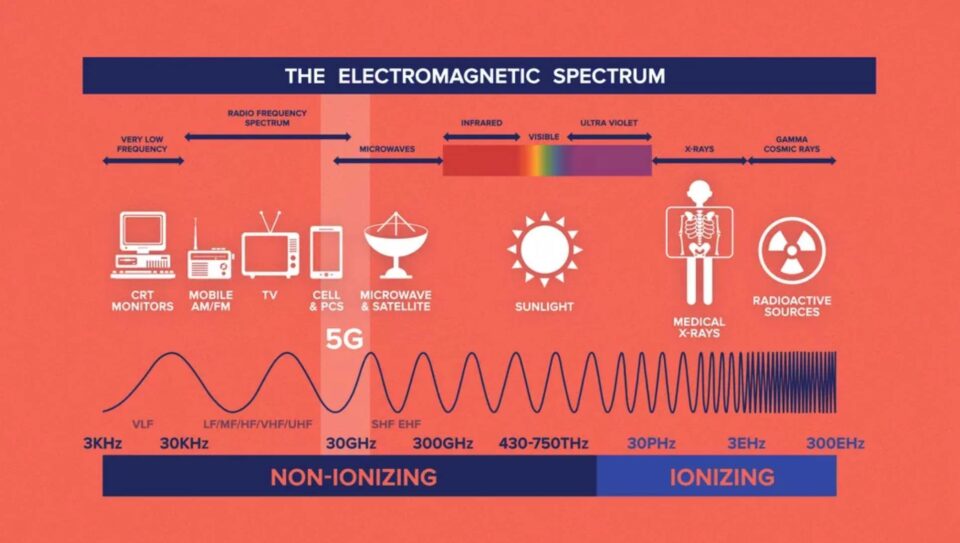
Scientists creating a network to triangulate and pinpoint lightning strikes around the world are using a very narrow band of radio waves to detect the phenomena over long distances. The small network of very low frequency (VLF) receivers includes stations in the Antarctic, including at Palmer Station. VLF generally refers to radio frequencies in the range of 3 to 30 kilohertz.